CONCLUSIONS In addition to taskbased fMRI, seedbased analysis of restingstate fMRI represents an equally effective method for supplementary motor area localization in patients with brain tumors, with the best results obtained with bilateral hand motor region seedingSCA = seedbased correlation analysis;The map represents a restingstate functional connectivity analysis performed on 1,000 human subjects, with the seed placed at the currently selected location Thus, it displays brain regions that are coactivated across the restingstate fMRI time series with the seed voxel Values are pearson correlations (r)

Predicting The Fmri Signal Fluctuation With Echo State Neural Networks Trained On Vascular Network Dynamics Biorxiv
Seed region fmri
Seed region fmri-However, it is known that taskrelated BOLD fMRI is susceptible to the locations o f large vesselsThe seed region time course for each participant was then regressed voxelwise against the participant's fMRI time course using the entire brain as the search space This approach reveals the strength of functional connectivity with respect to the seed region



Resting State Fmri Wikipedia
However, it is known that taskrelated BOLD fMRI is susceptible to the locations o f large vessels 1The seed region was at x=0, y=−8 and z=58 (blue circle) For Case 2 with complete left brachial plexopathy, restingstate fMRI could not reveal right cortical sensorimotor areas corresponding to the hand and arm at 2 months after injuries The seed region was at x=0, y=0 and z=56 (blue circle)FSL fMRI Resting State Seedbased Connectivity The seed region will be the Posterior Cingulate Gyrus You will identify the seed region using the HarvardOxford Cortical Atlas To start FSL, type the following in the terminal fsl & NB
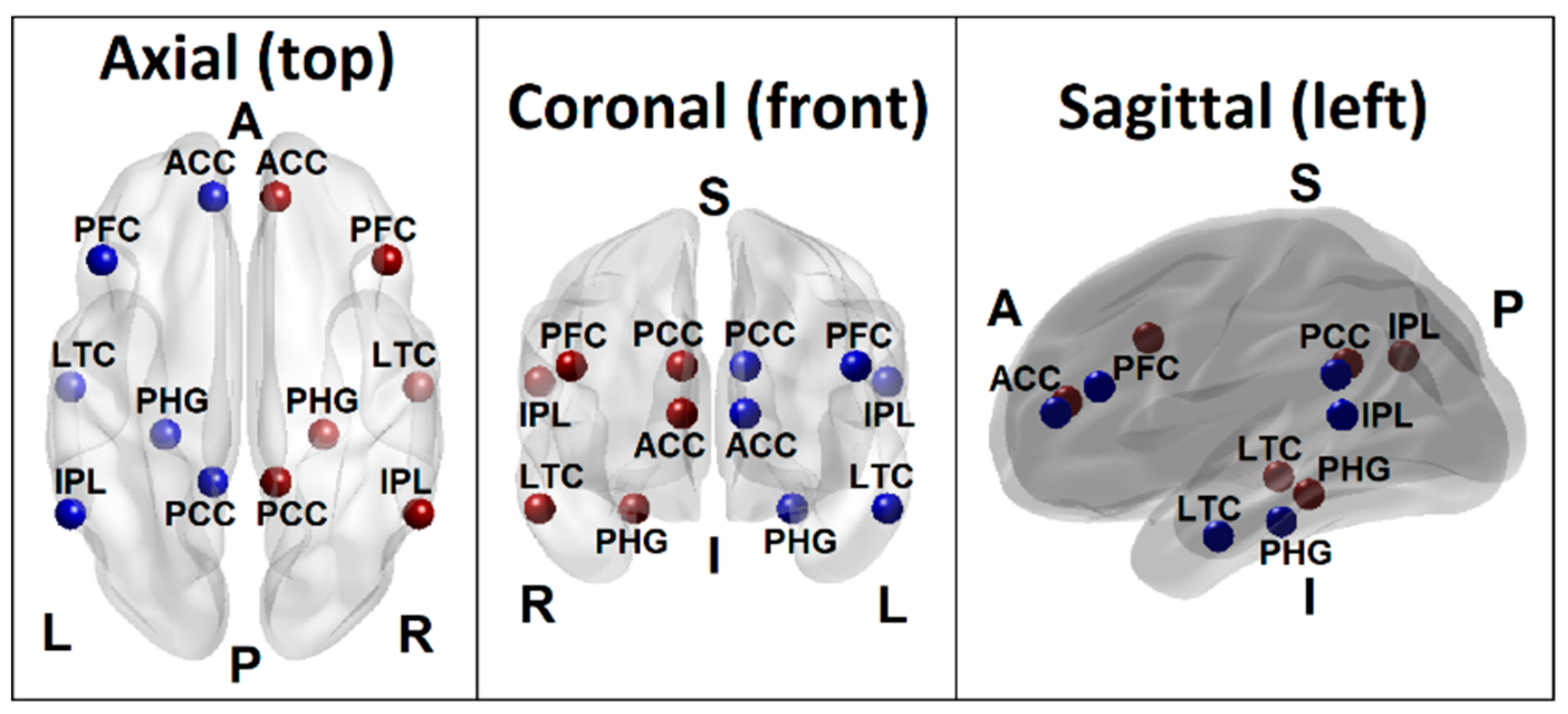
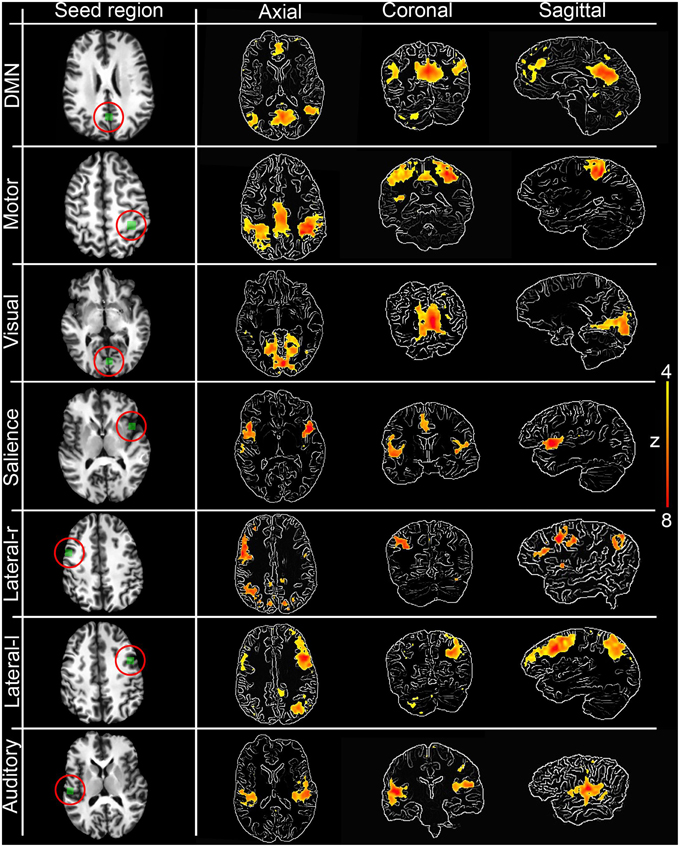
The seedbased approach extracts information from a specific brain region, called a "seed" region, and computes the similarity between information from the seed and all other brain region to obtain a brain network pattern Despite their popularity, seedbased correlation analyses have limitations such that they should require a priorIn investigations of the brain's resting state using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), a seedbased approach is commonly used to identify brain regions that are functionally connected The seed is typically identified based on anatomical landmarks, coordinates, or the location of brain activity during a separate task(A) Posterior cingulate seed (PCC) region (B) Correlation map created from the seed using the entire 10 minute time series (C) Correlation maps created over 32s temporal windows centered at the time points in the connected figures D and E (D) Sample time series from the seed region (red) and a voxel at the green crosshairs (motor cortex region)
Similar to conventional taskrelated fMRI, the BOLD fMRI signal is measured throughout the experiment (panel a) Conventional taskdependent fMRI can be used to select a seed region of interest (panel b) To examine the level of functional connectivity between the selected seed voxel i and a second brain region j (for example a region in theResting state (RS) connectivity has been increasingly studied in healthy and diseased brains in humans and animals This paper presents a new method to analyze RS data from fMRI that combines multiple seed correlation analysis with graphtheory (MSRA) We characterize and evaluate this new method in relation to two other graphtheoretical methods and ICAOr using multivariate methods, such as independent component analysis (ICA)


Magnetism Questions And Answers In Mri



Functional Connectomics From Resting State Fmri Trends In Cognitive Sciences
It relies on multiple seed correlation maps the mean timecourse of a seed region per brain region was correlated with the timecourse of every voxel in the brain resulting in one correlation volume per brain region Seed regions were defined automatically as the 4 voxels nearest to the center of mass of each atlas brain region (5 voxel in total)Restingstate functional magnetic resonance imaging (rsfMRI) has emerged as a powerful technique for characterizing brain networks and functional connectivity (Beckmann et al, 05;The seed region was at x=0, y=−8 and z=58 (blue circle) For Case 2 with complete left brachial plexopathy, restingstate fMRI could not reveal right cortical sensorimotor areas corresponding to the hand and arm at 2 months after injuries The seed region was at x=0, y=0 and z=56 (blue circle)



The Human Brain Is Intrinsically Organized Into Dynamic Anticorrelated Functional Networks Pnas



Figure 4
VAN = ventral attention network SUBMITTED September 30, 19ACCEPTED November 13, 19 INCLUDE WHEN CITINGDOI /1911FOCUS Mapping cognitive and emotional networks in neurosurgical patients using restingRestingstate fMRI methodology is currently dominated by two complementary strategies, spatial independent components analysis (SICA) (Beckmann et al 05) and seedbased correlation mapping (Biswal et al 1995) Both strategies depend on the fact that spontaneous neural activity is correlated (coherent) within widely distributed regions ofSUMMARY Restingstate fMRI was first described by Biswal et al in 1995 and has since then been widely used in both healthy subjects and patients with various neurologic, neurosurgical, and psychiatric disorders As opposed to paradigm or taskbased functional MR imaging, restingstate fMRI does not require subjects to perform any specific task The lowfrequency oscillations of the resting


Resting State Functional Mri Everything That Nonexperts Have Always Wanted To Know American Journal Of Neuroradiology



Altered Resting State Functional Connectivity Of The Putamen And Internal Globus Pallidus Is Related To Speech Impairment In Parkinson S Disease Manes 18 Brain And Behavior Wiley Online Library
FMRI is also too slow to capture all of the changes in the brain Each scan requires a second or two, enough time for a neuron to fire more than a hundred times That means it can't provide aRestingstate fMRI methodology is currently dominated by two complementary strategies, spatial independent components analysis (SICA) (Beckmann et al 05) and seedbased correlation mapping (Biswal et al 1995) Both strategies depend on the fact that spontaneous neural activity is correlated (coherent) within widely distributed regions ofFor each seed location, a sphere of 6mm radius was defined as the seed region and a reference time course was generated by averaging the time courses over the voxels within the region



Exploring Distinct Default Mode And Semantic Networks Using A Systematic Ica Approach Sciencedirect



Predicting The Fmri Signal Fluctuation With Echo State Neural Networks Trained On Vascular Network Dynamics Biorxiv
How to perform ROI analysis in the fMRI package SPM More details about the commands can be found here http//andysbrainblogblogspotcom/14/07/quickandRSN = restingstate network;Biswal et al, the time course of the seed region, values in the first column of Π^ are the partial correlation coefficients between the seed region and every


Brain Sciences Free Full Text Random Forest Classification Of Alcohol Use Disorder Using Fmri Functional Connectivity Neuropsychological Functioning And Impulsivity Measures Html


Frontiers 3d Interactive Tractography Informed Resting State Fmri Connectivity Neuroscience
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (functional MRI or fMRI) is a specific magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) procedure that measures brain activity by detecting associated changes in blood flow More specifically, brain activity is measured through low frequency BOLD signal in the brain Seedbased/Region of interest Another method of•Seed based correlation analysis (SCA;Therefore, to supplement the ICA results, a post hoc seed‐based functional connectivity analysis (FCA) was applied to the resting state fMRI data to examine the temporal coherence of the dlPFC region resulting from the ICA with the rest of the brain, using a seed‐to‐voxel regression strategy with this region as a source ROI



Fsl Fmri Resting State Seed Based Connectivity Neuroimaging Core 0 1 1 Documentation


Mri Resting State Fmri Carney Institute For Brain Science Brown University
A method for the evaluation of resting state functional MRI (fMRI) data from nuclear magnetic resonance tomographs that measures the correlation between a seed region signal time series and the signal time series in a plurality of voxels in the fMRI data comprising the steps of performing fMRI measurements to create a series of fMRI data with N time points using a sampling interval Δt that is equal to or shorter than the Nyquist sampling interval 1/(2f) required for sampling a periodicNote In this example, Biswal had used the left motor cortex as a seed region, which was then correlated with all of the other voxels in the brain also called a wholebrain analysis This type of correlation analysis is common, although some researchers may choose to restrict their correlation analysis between the seed region and a region of interestA voxelwise FC analysis of each ROI was performed for the preprocessed fMRI data For each subject and each seed region (namely ROI), a FC map of the whole brain was obtained by computing the correlation coefficients between the averaged time series of seed region and the time series of the remaining whole brain voxels


The Role Of Resting State Functional Mri For Clinical Preoperative Language Mapping Cancer Imaging Full Text


Identifying Resting State Networks From Fmri Data Using Icas By Gili Karni Towards Data Science
A seedtovoxel–based functional connectivity analysis was performed by computing the temporal correlation between the blood oxygen level–dependent signals to create a correlation matrix showing connectivity from the seed region to all other voxels in the brain by using the functional connectivity toolbox (CONN, version 13L) implemented inThe main way in which restingstate fMRI has been used is in computing restingstate functional connectivityThe majority of restingstate functional connectivity studies use univariate seedbased correlation methods, as appears in the original functional connectivity paper by Biswal and colleagues—that is, the correlation between the time courses extracted from a seed region and from theTo better understand intrinsic brain connections in major depression, we used a neuroimaging technique that measures resting state functional connectivity using functional MRI (fMRI) Three different brain networks—the cognitive control network, default mode network, and affective network—were investigated Compared with controls, in depressed subjects each of these three networks had



Using Informational Connectivity To Measure The Synchronous Emergence Of Fmri Multi Voxel Information Across Time Protocol



Seed Regions And Fmri Connectivity Results Image Eurekalert Science News
FMRI is also too slow to capture all of the changes in the brain Each scan requires a second or two, enough time for a neuron to fire more than a hundred times That means it can't provide aPET approach vs fMRI approach Because the contrast we used to select the seed region is not the same as the contrast we are interested in in the PPI analysis, our regressors are now looking a lot more orthogonal see Figure below) 1704 1328Seedbased connectivity metrics characterize the connectivity patterns with a predefined seed or ROI (Region of Interest) These metrics are often used when researchers are interested in one, or a few, individual regions and would like to analyze in detail the connectivity patterns between these areas and the rest of the brain



Abnormal Amygdala Resting State Functional Connectivity In Adults And Adolescents With Major Depressive Disorder A Comparative Meta Analysis Ebiomedicine


Fmri Becomes Big Big Science Citation Needed
FMRI'S fMRI is a technique of brain mapping that relies on the flow of blood in response to brain activity during tasks such as tapping a table, listening to music, talking to someone, reading, basically any kind of stimulation In order for an fMRI to work, it relies on the blood oxygen level dependant contrast (BOLD)Interesting idea In theory, almost any brain region can be used as a seed region for restingstate functional connectivity studies In practice, I think the SCN is going to be trickyTypical FMRI data analysis " Massively univariate (voxelwise) regression y = Xβε " Relatively robust and reliable " May infer regions involved in a task/state, but can't say much about the details of a network !


Predicting Functional Networks From Region Connectivity Profiles In Task Based Versus Resting State Fmri Data
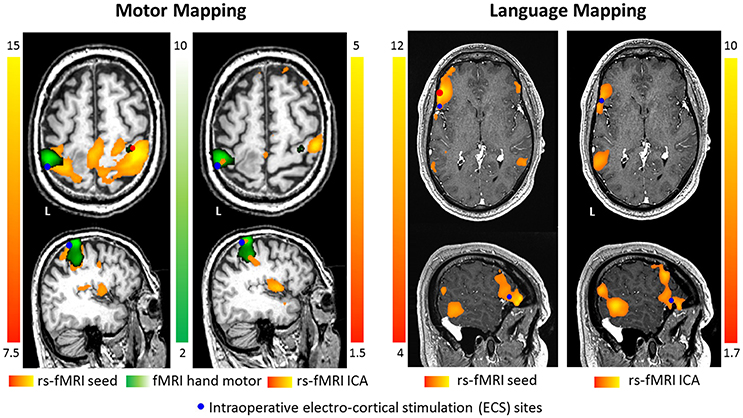


Frontiers Pre Surgical Brain Mapping To Rest Or Not To Rest Neurology
To this end, we selected the restingstate fMRI data of high (n = 22) and lowlevel creativity groups (n = 22), and adopted the voxelwise, seedwise, and dynamic functional connectivity toCalculate group average of Fisher z scores 4Perform two sample ttest of group averagesSeed = region of interest) Temporal correlation between the time course of every voxel in the brain and the time course from a seed voxel • hypothesisdriven a priori selection of a voxel, cluster, or atlas • the extracted time series is used as regressors in a GLM analysis • univariate approach
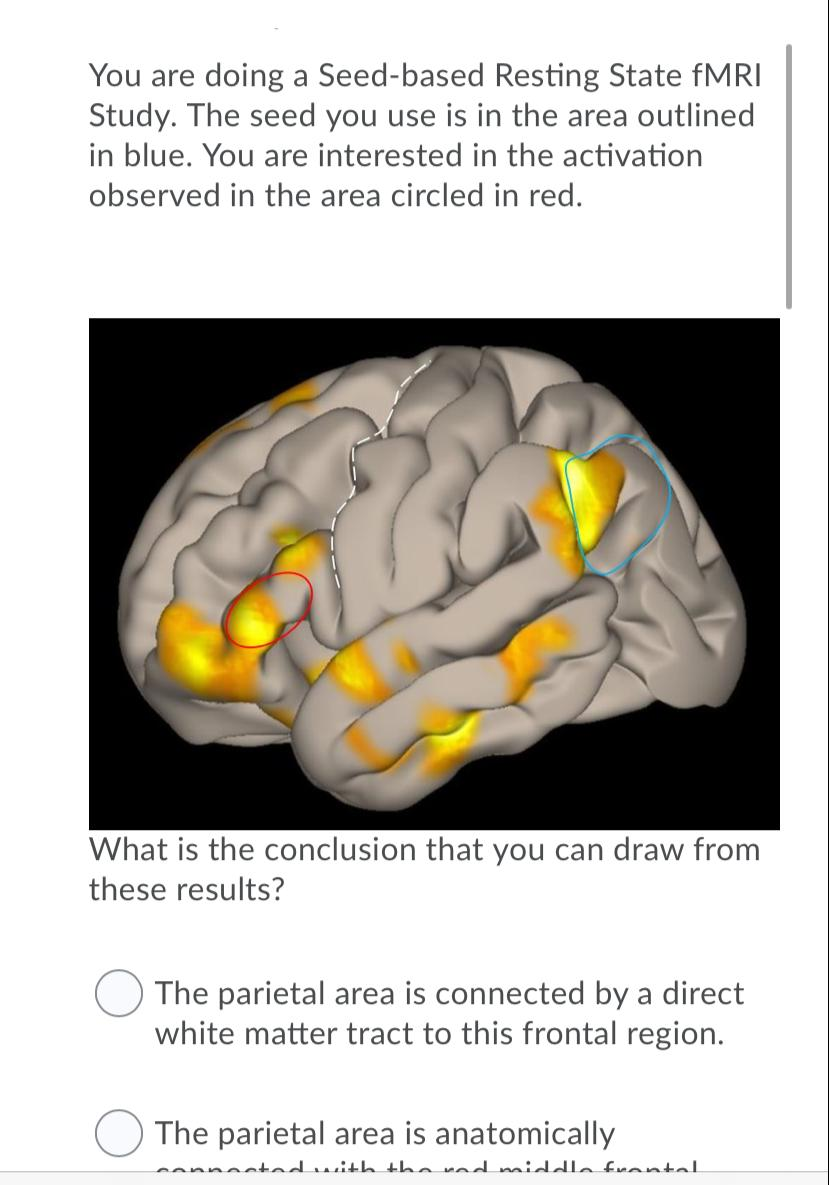


Solved You Are Doing A Seed Based Resting State Fmri Stud Chegg Com


Fmri Ecog Correlates Carl Hacker1 Abraham Z Snyder2 3 Mrinal Pahwa1 Maurizio Corbetta2 And Eric C Leuthardt1 1neurosurgery Washington University School Of Medicine Saint Louis Mo United States 2neurology Washington University School
Many functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) analyses of the resting state rely on the identification of a seed region based on location of significant activity during a separate task;However, in light of the present results, other potential biomarkers might be more sensitive to premanifest Huntington's pathology than resting fMRI correlations (Aylward et al, 1996;Majid et al, 11;Tabrizi et al, 11)It is also possible that resting fMRI correlations differ with preHD when some other region is selected as the seedOf the six seed regions and all other voxels in the brain were then computed for each individual The results from a single individual for a seed region in the PCC are shown in Fig 1 Fig 1 Uppershows the regional distribution of correlation coefficients, and Fig 1 Lower shows time courses for the PCC seed region
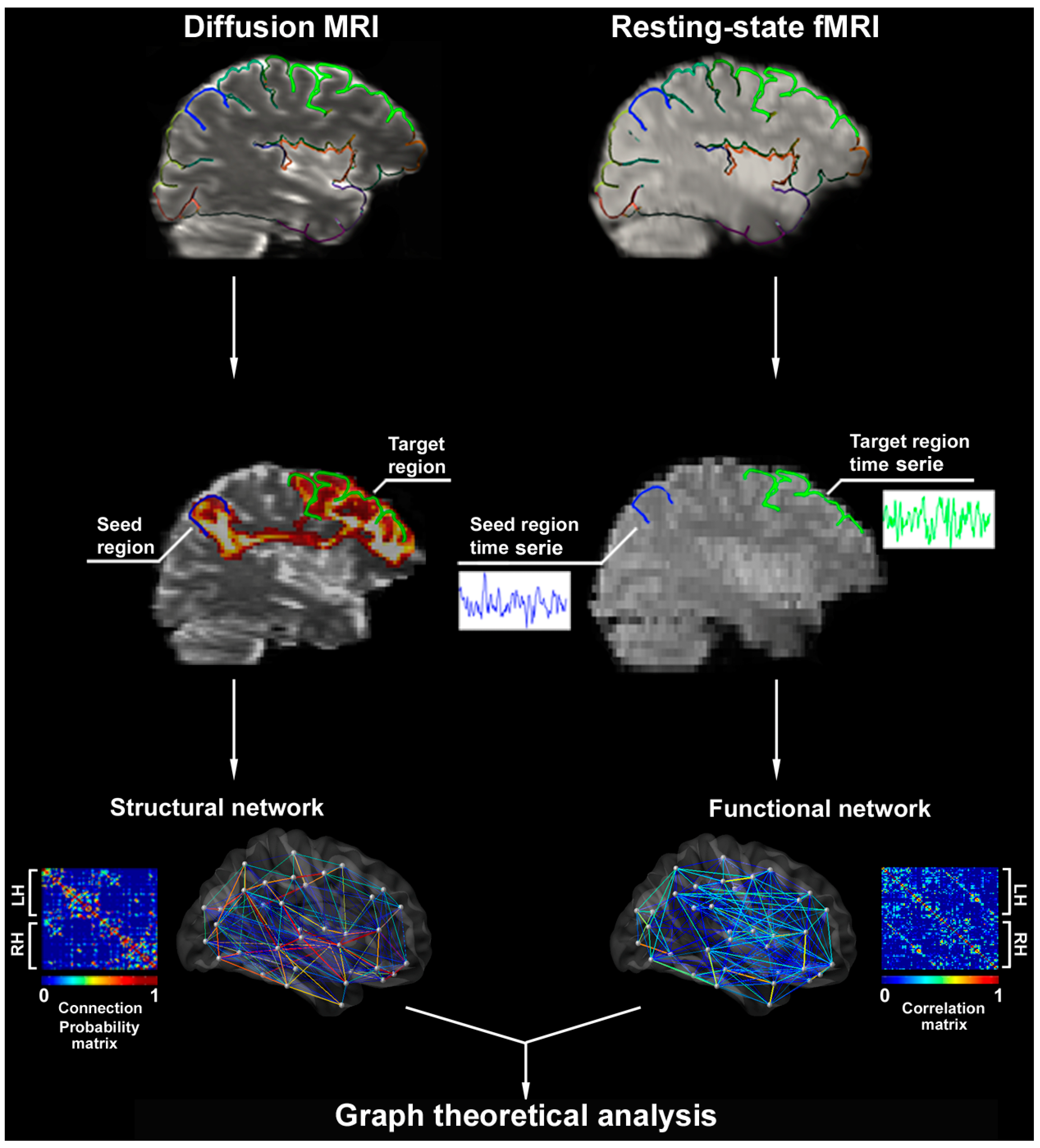


Brain Sciences Free Full Text Contributions Of Imaging To Neuromodulatory Treatment Of Drug Refractory Epilepsy Html



There Were Significant Fc Fmri Values Relative To The Pcc Seed Region Download Scientific Diagram
Summarize regions by average time course 2For each subject, calculate correlations between seed region and other regions of interest 3Transform Pearson correlations by Fisher's z;The middle panel shows a timeseries extracted from a seed region The bottom panel shows the interaction regressor, created by multiplying the above regressors Note how the 1's, when multiplied by the seed timeseries, invert the sign of the timeseries if the timeseries is going down, in the interaction regressor it will go upIn the present study, the strength of rsFC with the left inferior and middle frontal gyri as seed regions was compared between INT and CONT using twosample ttestsAs illustrated in Fig 1, significantly higher rsFC was identified in INT than in CONT between the left inferior frontal gyrus seed centered at (− 52, 12, 0) and the temporal pole, and between the left inferior frontal gyrus seed



Altered Hypothalamic Functional Connectivity In Cluster Headache A Longitudinal Resting State Functional Mri Study Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry


Plos One Probing The Interoceptive Network By Listening To Heartbeats An Fmri Study
The seedbased approach extracts information from a specific brain region, called a "seed" region, and computes the similarity between information from the seed and all other brain region to obtain a brain network pattern Despite their popularity, seedbased correlation analyses have limitations such that they should require a priorFor each seed location, a sphere of 6mm radius was defined as the seed region and a reference time course was generated by averaging the time courses over the voxels within the region The rsfMRI connectivity map was computed using Pearson correlation between the reference time course and that of each voxel in the brain (voxel size = 375Many functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) analyses of the resting state rely on the identification of a seed region based on location of significant activity during a separate task;



Use Of Resting State Fmri In Planning Epilepsy Surgery



Changes In Resting State Functional Brain Activity Are Associated With Waning Cognitive Functions In Hiv Infected Children Sciencedirect
Brain functional connectivity (FC) is often assessed from fMRI data using seedbased methods, such as those of detecting temporal correlation between a predefined region (seed) and all other regions in the brain;Resting state fMRI (rsfMRI or RfMRI) is a method of functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) that is used in brain mapping to evaluate regional interactions that occur in a resting or tasknegative state, when an explicit task is not being performed A number of restingstate conditions are identified in the brain, one of which is the default mode networkNetwork analysis " Information o Seed region, some or all regions in a network
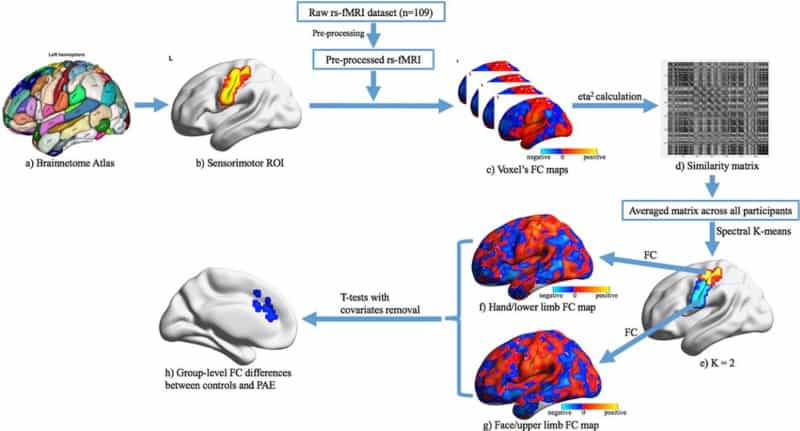


Pre Natal Alcohol Exposure Alters Functional Connectivity Physics World



Assessing Functional Connectivity In The Human Brain By Fmri Abstract Europe Pmc
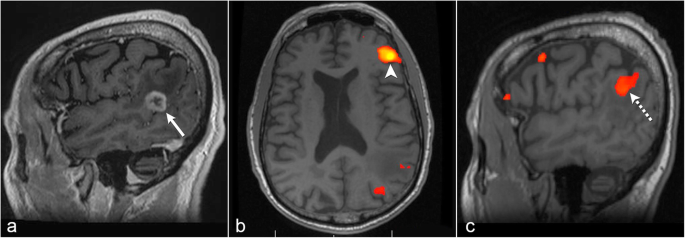
Restingstate fMRI using the left inferior frontal gyrus as the seed region demonstrated strong correlations with right inferior frontal gyri as well as bilateral Wernicke's area (purple circles) In this case, the conclusion was also a bilateral representation of language processingState functional magnetic resonance imaging (rsfMRI) is an emerging AD biomarker that provides a noninvasive method to measure subtle functional changes in the another region or seed to analyze seedtoseed connectivity Th e sensorymotor ICN was fi rst demonstrated in fMRI by using a seedbased methodology 3, as was theSN = salience network;



An Analytical Workflow For Seed Based Correlation And Independent Component Analysis In Interventional Resting State Fmri Studies Sciencedirect



Seed Based Resting State Fmri Functional Connectivity Matrices
Are dependent on the seed region locations, the additional challenge of consistent seed placement arises in group analysis We propose clustering as a means to automatically identify candidate seed time courses based on the fMRI data Independent Component Analysis (ICA) 4, 5 is an alternativeRsfMRI = restingstate fMRI;When the voxels of the seed region were included in the task‐free fMRI analysis, the difference between task and task‐free fMRI did not change at a supra‐threshold of 5,000 and 1,000 voxels, while it decreased from 11 to 6% at a supra‐threshold of 100 voxels



Spatial Maps For Seed Based Correlations With The Dorsal Poste Ured Download Scientific Diagram



Seed Based Resting State Fmri Analysis In Freesurfer Ppt Download
1Identify seed region and regions of interest;



Resting State Fmri Wikipedia
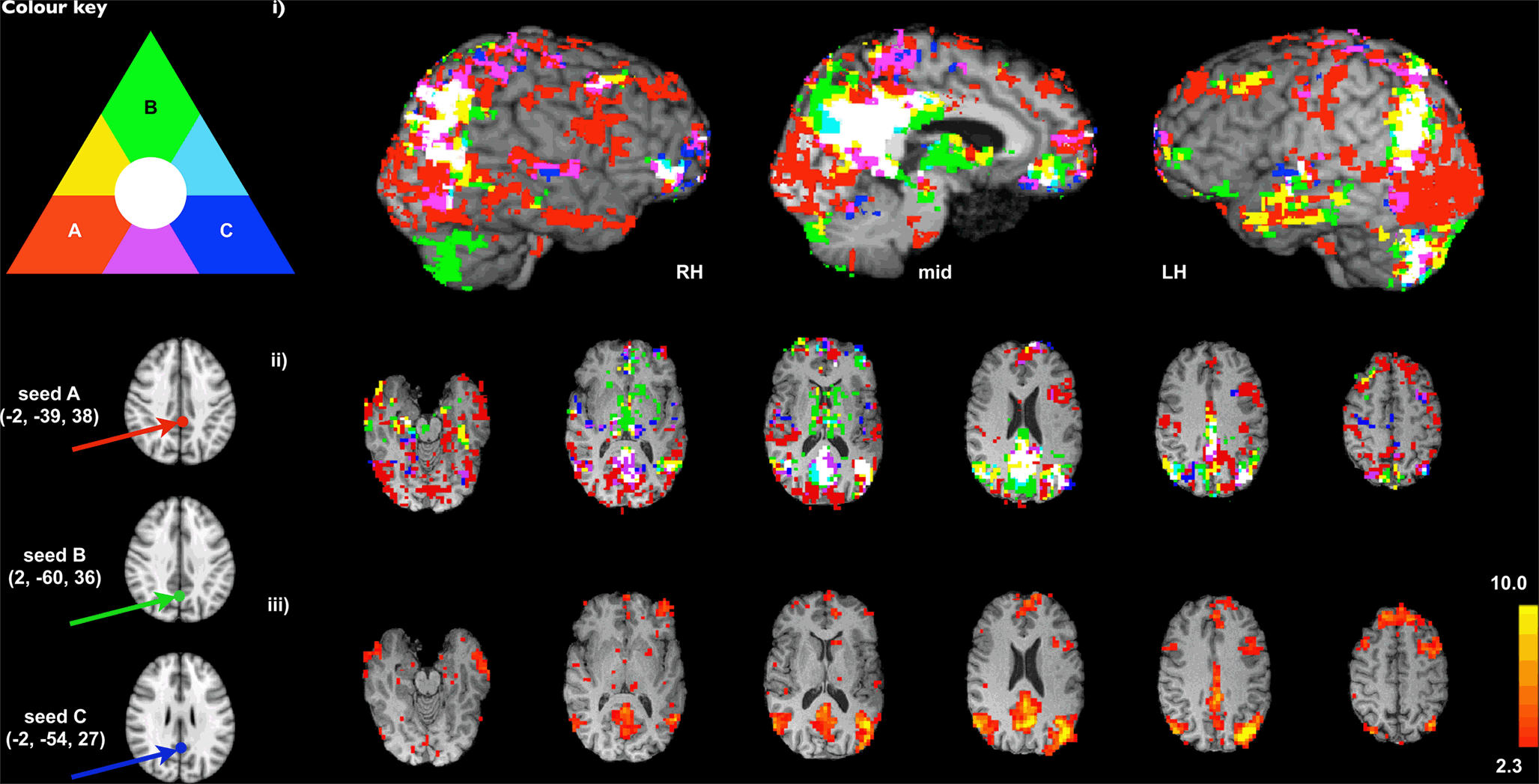


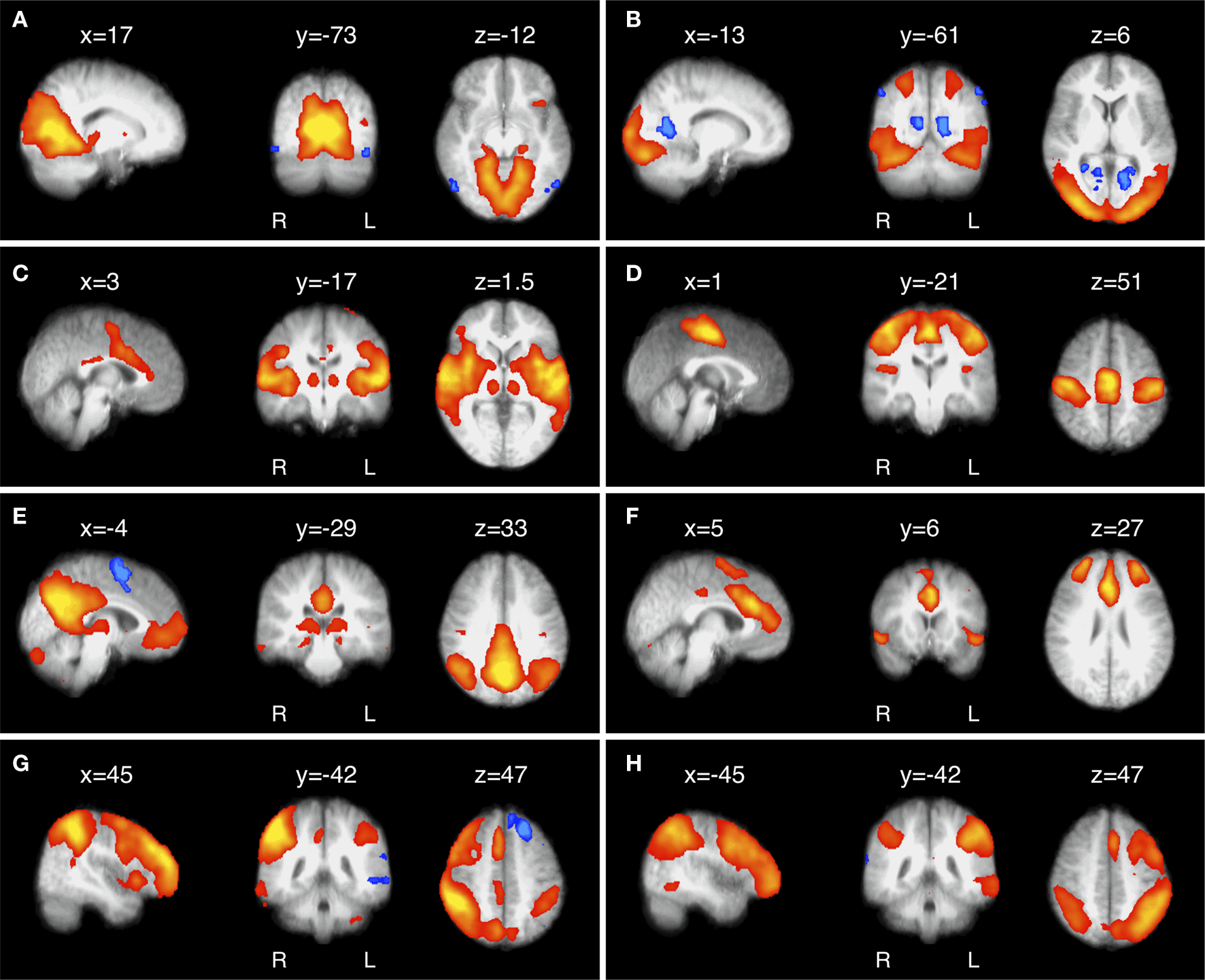
Frontiers Advances And Pitfalls In The Analysis And Interpretation Of Resting State Fmri Data Frontiers In Systems Neuroscience
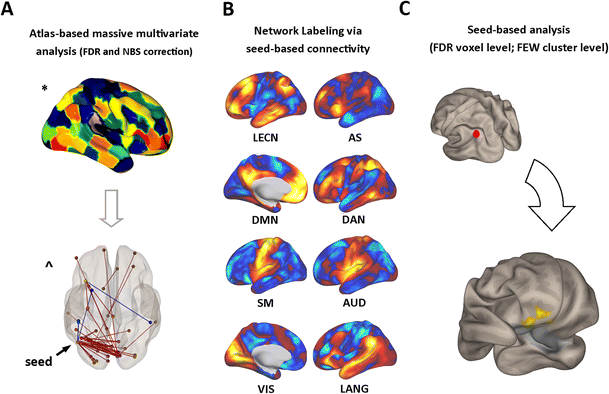


Figure 1 Brain Functional Connectivity Correlates Of Coping Styles Springerlink



Spatial Maps For Seed Based Correlations With The Dorsal Posterior Download Scientific Diagram



Characterizing The Spectrum Of Task Fmri Connectivity Approaches Ppt Download


Plos One Resting State Fmri Reveals Diminished Functional Connectivity In A Mouse Model Of Amyloidosis



Andy S Brain Blog
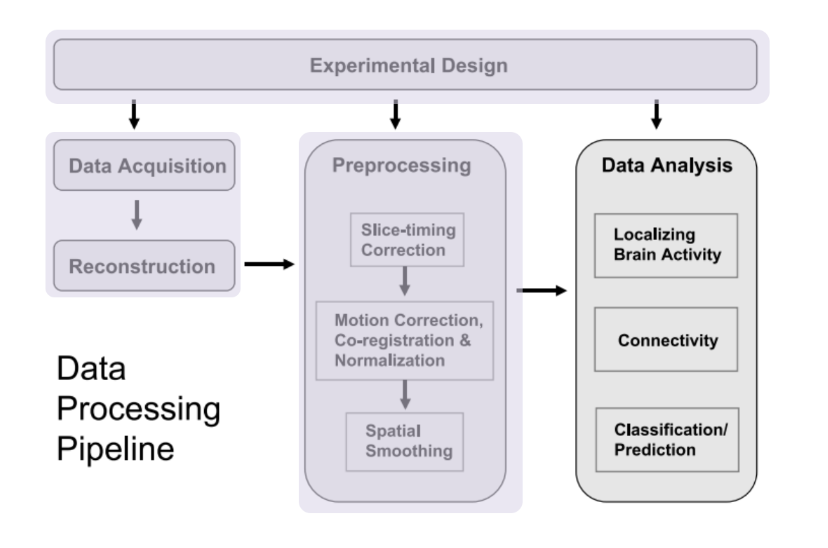


Identifying Resting State Networks From Fmri Data Using Icas By Gili Karni Towards Data Science



Fmri Dr Micah Allen


Ohbm Ondemand How To Resting State Fmri Analysis Organization For Human Brain Mapping
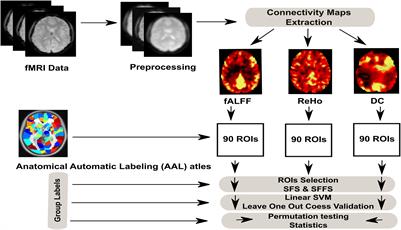


Frontiers Machine Learning Based Classification Of Resting State Fmri Features Exemplified By Metabolic State Hunger Satiety Human Neuroscience



Seed Regions Of The Seed Based Resting State Analysis Seed Regions And Download Scientific Diagram



Fsl Fmri Resting State Seed Based Connectivity Neuroimaging Core 0 1 1 Documentation


Resting State Functional Mri Everything That Nonexperts Have Always Wanted To Know American Journal Of Neuroradiology


Seizure Frequency Can Alter Brain Connectivity Evidence From Resting State Fmri Ajnr Blog



Time Varying Functional Network Information Extracted From Brief Instances Of Spontaneous Brain Activity Pnas
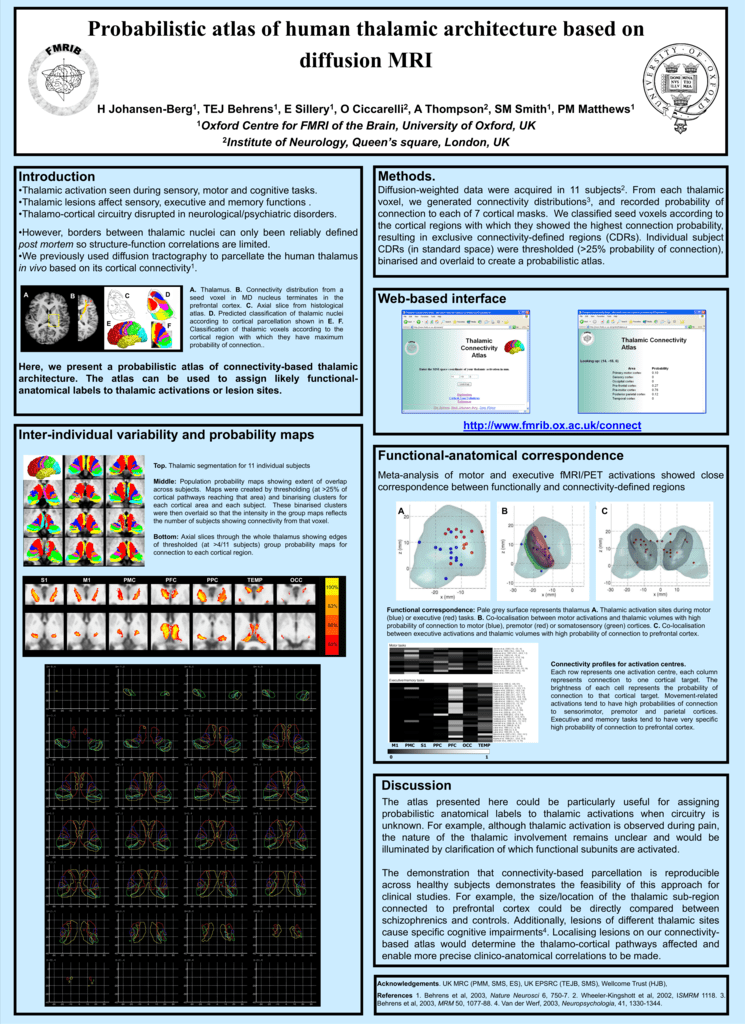


A Functional Mri Study A Ploghaus1 2 I Tracey2 Pm Matthews2 S


Functional Connectivity Signatures Of Parkinson S Disease Ios Press
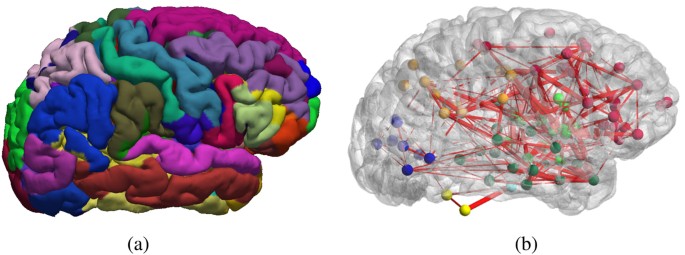


Function Specific And Enhanced Brain Structural Connectivity Mapping Via Joint Modeling Of Diffusion And Functional Mri Scientific Reports



Resting State Fmri Wikipedia


Ppt Fmri Connectivity Analysis In Afni Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Mapping Cognitive And Emotional Networks In Neurosurgical Patients Using Resting State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Neurosurgical Focus Volume 48 Issue 2



Functional Connectivity Of Left Auditory Cortex Ppi Seed Region In Different Visual Wm Load Conditions



Oscillatory Brain States Govern Spontaneous Fmri Network Dynamics Biorxiv



Maps Of Seed Based Resting State Fmri Functional Connectivities The Download Scientific Diagram



Effects Of Early And Late Bilingualism On Resting State Functional Connectivity Journal Of Neuroscience


The Role Of Resting State Functional Mri For Clinical Preoperative Language Mapping Cancer Imaging Full Text



Rsfc Correlations Seed Regions Consisted Of The 5 Functional And 2 A Download Scientific Diagram



There Were Significant Fc Fmri Values Relative To The Pcc Seed Region Download Scientific Diagram



Fsl Fmri Resting State Seed Based Connectivity Neuroimaging Core 0 1 1 Documentation



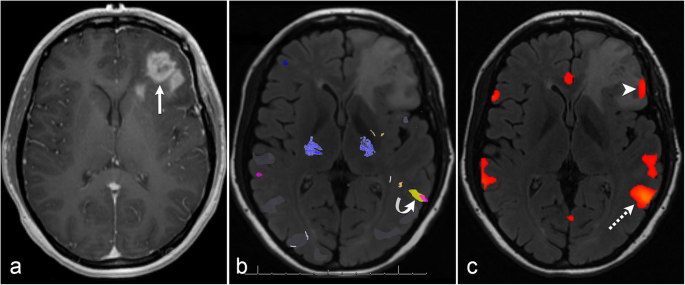
Sensorimotor Cortical Changes Assessed With Resting State Fmri Following Total Brachial Plexus Root Avulsion Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry



Figure 3 From A Window Into The Brain Advances In Psychiatric Fmri Semantic Scholar


Resting State Seed Based Analysis An Alternative To Task Based Language Fmri And Its Laterality Index American Journal Of Neuroradiology



Fsl Fmri Resting State Seed Based Connectivity Neuroimaging Core 0 1 1 Documentation


Frontiers Advances And Pitfalls In The Analysis And Interpretation Of Resting State Fmri Data Frontiers In Systems Neuroscience
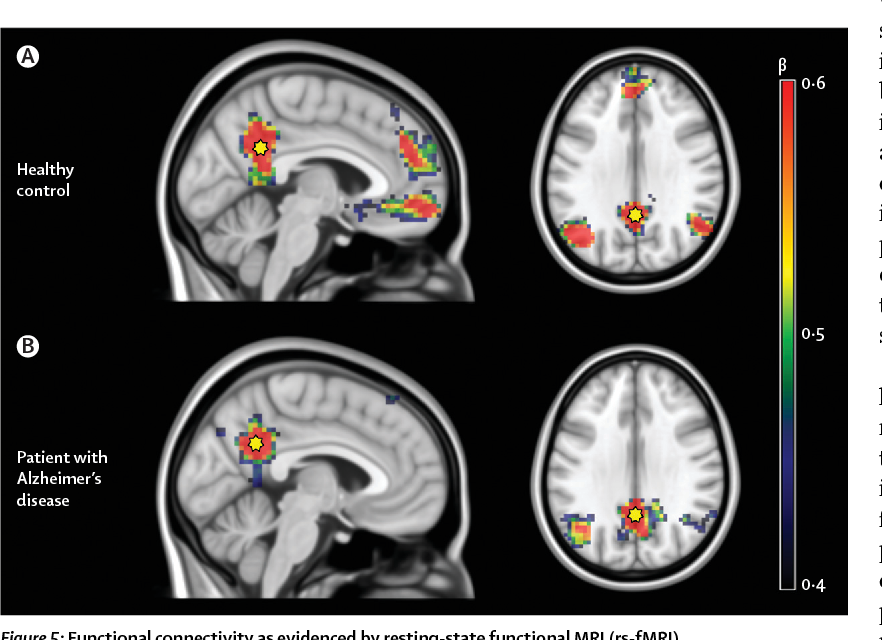


Figure 5 From Multimodal Imaging In Alzheimer S Disease Validity And Usefulness For Early Detection Semantic Scholar


Resting State Functional Mri Everything That Nonexperts Have Always Wanted To Know American Journal Of Neuroradiology
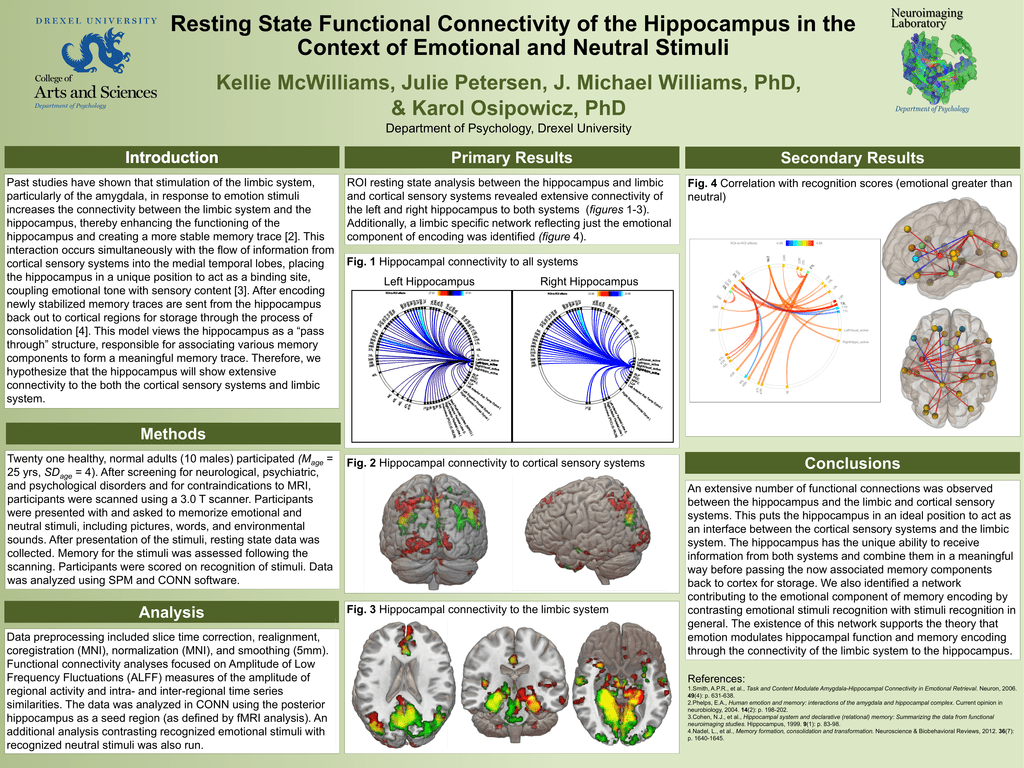


Resting State Functional Connectivity Of The Hippocampus In The



Emergence Of Resting State Networks In The Preterm Human Brain Pnas
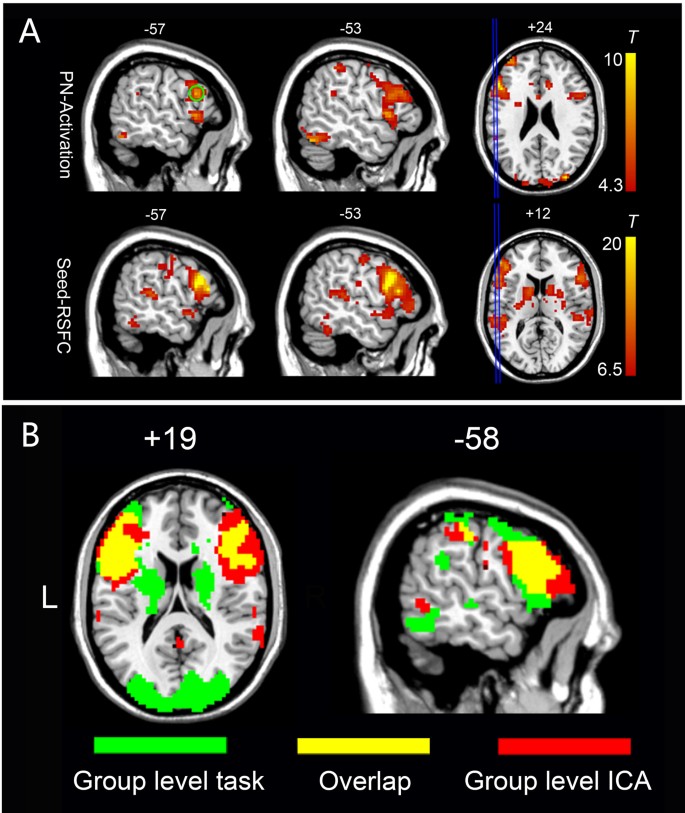


An Automated Method For Identifying An Independent Component Analysis Based Language Related Resting State Network In Brain Tumor Subjects For Surgical Planning Scientific Reports



Figure 1 From Optimization Of Anesthesia Protocol For Resting State Fmri In Mice Based On Differential Effects Of Anesthetics On Functional Connectivity Patterns Semantic Scholar



Combining Prospective Acquisition Correction Pace With Retrospective Correction To Reduce Motion Artifacts In Resting State Fmri Data Lanka 19 Brain And Behavior Wiley Online Library
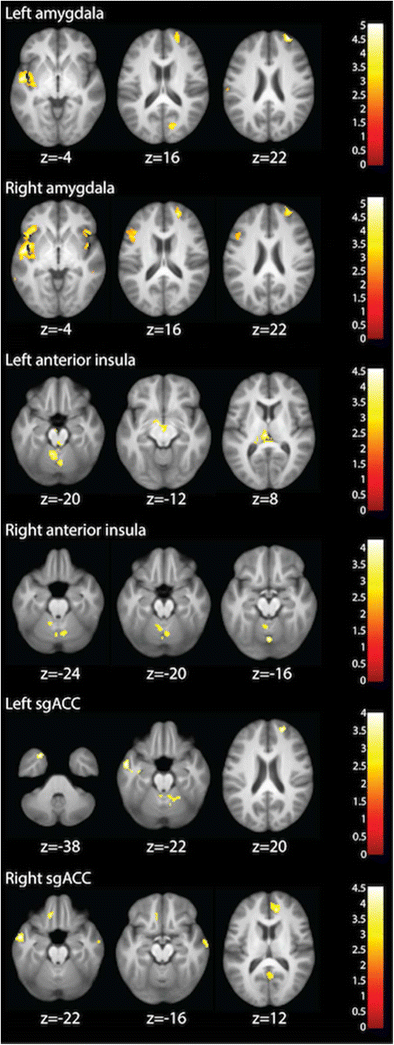


Integrated Cross Network Connectivity Of Amygdala Insula And Subgenual Cingulate Associated With Facial Emotion Perception In Healthy Controls And Remitted Major Depressive Disorder Springerlink
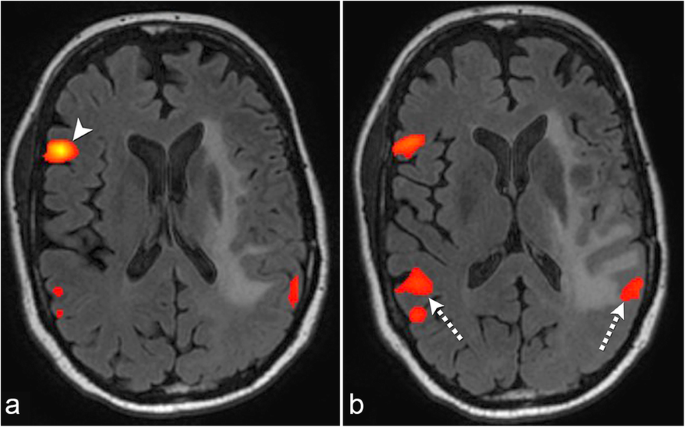


The Role Of Resting State Functional Mri For Clinical Preoperative Language Mapping Cancer Imaging Full Text


Magnetism Questions And Answers In Mri



Resting State Fmri Wikipedia



Mapping Cognitive And Emotional Networks In Neurosurgical Patients Using Resting State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging In Neurosurgical Focus Volume 48 Issue 2



Machine Learning In Resting State Fmri Analysis Deepai



A Window Into The Brain Advances In Psychiatric Fmri



Chronic And Acute Nicotine Alters Intra And Inter Regional Resting State Fmri Of The Vmpfc



Concurrent Eeg And Fmri Derived Functional Connectomes Exhibit Linked Dynamics Biorxiv


Plos One Unravelling The Intrinsic Functional Organization Of The Human Striatum A Parcellation And Connectivity Study Based On Resting State Fmri



Rapid Precision Functional Mapping Of Individuals Using Multi Echo Fmri Sciencedirect


Resting State Functional Mri Everything That Nonexperts Have Always Wanted To Know American Journal Of Neuroradiology



Resting State Fmri Wikipedia



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿